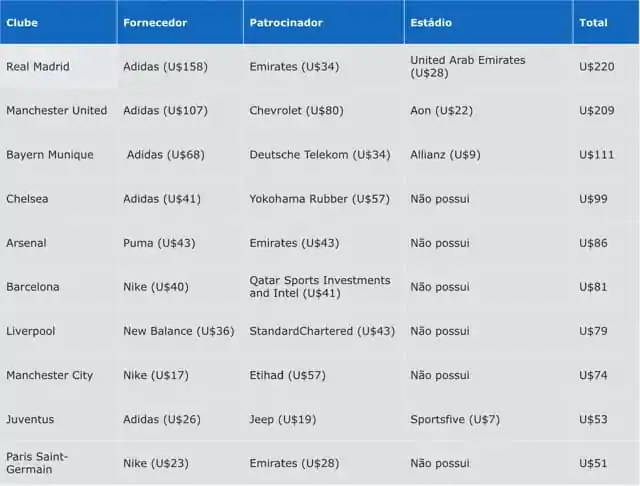
Sponsorship contracts are a cornerstone of modern soccer. They provide vital financial support to clubs, players, and competitions while offering businesses global exposure through one of the most watched sports in the world. These contracts are more than just logo placements on jerseys; they are strategic partnerships that involve detailed negotiations, legal frameworks, and marketing initiatives.
Understanding how these sponsorship deals work can shed light on the commercial side of soccer, offering insights into how money flows through the sport, what brands are looking for, and how clubs benefit. In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of sponsorship contracts in soccer, from types and structures to negotiation and execution.
The Role of Sponsorship in Soccer
Soccer is a multi-billion-dollar industry. Much of its financial success hinges on sponsorships. Clubs, leagues, tournaments, and even individual players rely heavily on corporate sponsors to fund operations, player salaries, infrastructure, and community projects.
Sponsorship can:
- Increase a brand’s visibility and global reach.
- Offer credibility and prestige through association with well-known teams.
- Enable clubs to grow financially and competitively.
- Support grassroots and community initiatives.
Key Types of Sponsorships in Soccer
Sponsorship contracts in soccer vary based on the party being sponsored and the nature of the deal. Here are the most common types:
1. Kit Sponsorship
The most visible form, this includes logos on jerseys, shorts, socks, and training gear. Examples include Emirates and Arsenal or Chevrolet and Manchester United.
2. Stadium Naming Rights
Brands pay to have their name associated with a stadium. Examples include Etihad Stadium (Manchester City) and Allianz Arena (Bayern Munich).
3. Official Partner Agreements
These involve official suppliers or partners for items like beverages, telecommunications, or even insurance. They gain branding opportunities, hospitality packages, and rights to use the club’s image.
4. League or Tournament Sponsorships
Competitions like the English Premier League or UEFA Champions League have title or official sponsors that fund the event in return for exposure across games, media, and advertising.
5. Individual Player Sponsorships
Brands often sign endorsement deals with star players to leverage their image and reach. For example, Cristiano Ronaldo with Nike or Lionel Messi with Adidas.
Structure of a Sponsorship Contract
Sponsorship contracts in soccer include several key components to outline the rights, responsibilities, and expectations of both parties:
1. Duration and Term
The contract states how long the sponsorship will last, often ranging from one season to multiple years.
2. Financial Compensation
This includes the sponsorship fee and any performance-based bonuses or incentives. It may also include in-kind support such as providing equipment.
3. Branding Rights
Details where and how the sponsor’s logo and brand will be used, such as on uniforms, in stadiums, or across digital platforms.
4. Exclusivity
Sponsors often demand category exclusivity. For example, a beverage sponsor may require that no other beverage company partners with the same team.
5. Performance Clauses
These may relate to team performance, player appearances, or minimum advertising exposure. Failure to meet these can lead to penalties or contract termination.
6. Termination Clauses
These specify under what circumstances either party can end the agreement, such as breach of contract, financial issues, or reputational damage.
7. Legal and Compliance Requirements
The contract must comply with national laws and league regulations, including those related to advertising, fair competition, and ethical behavior.
The Negotiation Process
Negotiating a sponsorship contract is a complex process involving lawyers, marketing teams, financial experts, and club executives.
Steps in the Negotiation:
- Identifying Goals: Both sponsor and club define what they aim to achieve.
- Proposing Terms: The club offers a proposal outlining branding opportunities and associated costs.
- Due Diligence: Background checks and financial evaluations ensure compatibility and mitigate risks.
- Negotiation Meetings: Both sides discuss specifics including exposure, performance metrics, and legal considerations.
- Drafting the Contract: Lawyers draw up the legal agreement, covering all agreed terms.
- Approval and Signing: Once both parties approve, the contract is signed and the sponsorship begins.
Benefits for the Soccer Club
Sponsorships provide much-needed financial support, allowing clubs to:
- Acquire and retain star players.
- Invest in youth development.
- Upgrade facilities.
- Expand their global fanbase through sponsor-led marketing campaigns.
For example, a club that signs a major sponsor may use the funds to build a new training center, hire better coaches, or fund global tours.
Benefits for the Sponsor
Sponsors gain access to a passionate and global audience. Soccer fans often form emotional connections with their teams, and that loyalty can extend to associated brands.
Key benefits include:
- Brand Visibility: TV broadcasts, social media, and merchandise offer wide exposure.
- Targeted Marketing: Clubs offer demographic insights to tailor marketing.
- Content Creation: Sponsors can create campaigns featuring players or club icons.
- Hospitality and Networking: VIP access to matches and club events for clients or partners.
Risks and Challenges
Despite the benefits, sponsorships in soccer carry certain risks:
1. Reputational Risk
If a club becomes embroiled in scandal or performs poorly, the sponsor may suffer by association.
2. Lack of ROI
Without strategic execution, the sponsor may not achieve the expected return on investment.
3. Regulatory Hurdles
Leagues and governing bodies impose restrictions, such as bans on certain industries like gambling or alcohol in some regions.
4. Changing Market Conditions
Economic downturns or shifts in consumer behavior can affect the perceived value of the sponsorship.
Case Studies of Successful Sponsorships
Fly Emirates and Arsenal FC
This long-standing partnership included jersey branding, stadium signage, and joint marketing campaigns. Emirates gained worldwide visibility while Arsenal secured consistent financial support.
Red Bull and RB Leipzig
Red Bull’s investment went beyond sponsorship. They helped build the club from scratch, providing full financial and logistical support. The team rose rapidly through the German football league system.
Nike and Paris Saint-Germain (PSG)
Nike’s partnership with PSG includes not just team kits but collaborative apparel lines featuring star players like Neymar and Mbappé. The result is a mix of sports and lifestyle branding.
Digital Evolution of Sponsorships
In today’s digital age, soccer sponsorships are not limited to physical branding. Digital content and social media have become integral parts of sponsorship strategies.
Examples:
- Hashtag Campaigns: Promoted hashtags during live games.
- Influencer Collaborations: Players as social media influencers.
- Branded Content: Behind-the-scenes videos or interactive fan experiences.
This evolution allows sponsors to reach fans beyond the stadium, creating personalized and engaging content that builds loyalty.
Future Trends in Soccer Sponsorship
As technology and fan behavior evolve, so do sponsorship strategies. Here are a few emerging trends:
1. Sustainability and Social Impact
Sponsors are increasingly focused on environmental and social responsibility. Clubs are now aligning with brands that support green initiatives or community programs.
2. Data-Driven Sponsorships
Using data analytics, sponsors can measure engagement, brand recall, and conversion rates to optimize their campaigns.
3. Esports and Virtual Engagements
With the rise of FIFA esports and virtual fan experiences, new platforms for sponsorship are emerging.
4. Cryptocurrency and Blockchain
Some clubs are now partnering with crypto companies, offering fan tokens and blockchain-based collectibles.
Final Thoughts: A Win-Win Relationship
Sponsorship contracts in soccer are mutually beneficial agreements that support the sport’s financial ecosystem and enhance brand value for businesses. When executed well, these partnerships create opportunities for growth, innovation, and deeper fan engagement.
Whether you’re a marketer, sports executive, or simply a curious fan, understanding how these contracts work offers valuable insight into the commercial engine driving modern soccer.